Classification #
The chemicals and botanicals have been categorized in terms of their primary effect. This broadly reflects the approach taken by Erowid, and other online authorities.
The specific groupings are as follows:
PSYCHEDELICS #
This is a substance which alters perception and cognition, creating an experience which is different to ordinary consciousness, often significantly so.
The psychedelic state is often related to forms such as meditation, dreaming, yoga, near-death or out-of-body experiences, and access to other realms or dimensions of reality.
STIMULANTS #
Stimulants, or stims, enhance or improve mental and/or physical capability or function. Manifestations of this can include alertness, wakefulness, focus, and apparent increased energy. As a consequence, stimulants are sometimes referred to as uppers.
DISSOCIATIVES #
A dissociative produces a sense of detachment from normal sights, sounds and experiences of self. This dissociation from environment is often classified as a hallucinogenic experience.
INTOXICATING DEPRESSANTS #
Depressants induce depression of the central nervous system (CNS), which reduces arousal or stimulation. This slows down the activity of the brain and nervous system, with the physical and psychoactive effects often dependent upon dose. Intoxicants excite or stupefy to the point where physical and mental control is diminished.
Intoxicating depressants tend to combine these experiences, with their effects transforming and morphing towards the former, as the duration unfolds.
SYNTHETIC CANNABINOIDS #
Synthetic cannabinoids are synthesised substances which act upon cannabinoid receptors, creating effects which can be perceived as similar to the cannabis genus in one or more respects.
ONEIROGENS #
An oneirogen is widely considered to induce, enhance or promote lucid or vivid dreaming. It is sometimes defined as a substance that produces dream-like states of consciousness. These can be profound, and can manifest as realistic or abstract.
EMPATHOGENS & ENTACTOGENS #
Empathogens and entactogens tend to produce feelings of emotional communion and bonding with others, particularly in terms of empathy and oneness. This state is most widely reported with respect to MDMA, but is actually created via a substantial number of substances.
EUPHORIANTS #
These create a sense of euphoria, elation or bliss, sometimes in association with the empathy produced via an empathogen.
ANXIOLYTICS & SEDATIVES #
A sedative can produce a calming or relaxing effect, such that stress, irritability or agitation is reduced. In some cases sedatives can produce hypnotic anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects. Technically, sedatives are depressants, in that they induce depression of the central nervous system (CNS), although many also have antipsychotic properties.
NOOTROPICS #
Also referred to as smart drugs, nootropics are substances (chemical or botanical) that improve or enhance cognitive function, including memory and creativity.
DELIRIANTS #
This is a class of hallucinogen that induces an ‘acute confusional state’, as opposed to the more lucid state typified by classical psychedelics.
Deliriants generally produce unpleasant experiences, are often toxic, and are prone to expose the user to personal risk, which can be severe.
UNCLASSIFIED #
A number of substances produce effects which do not fit comfortably into any of the above. Some, for example, induce a combination of these, providing a very distinct experience. Others create differing effects as the experience unfolds.
Note that there are a variety of other approaches and definitions, and that most, like this one, introduce a degree of subjectivity.
The adjacent diagram presents one view of the relationships between different classifications and some of the most well known chemicals.
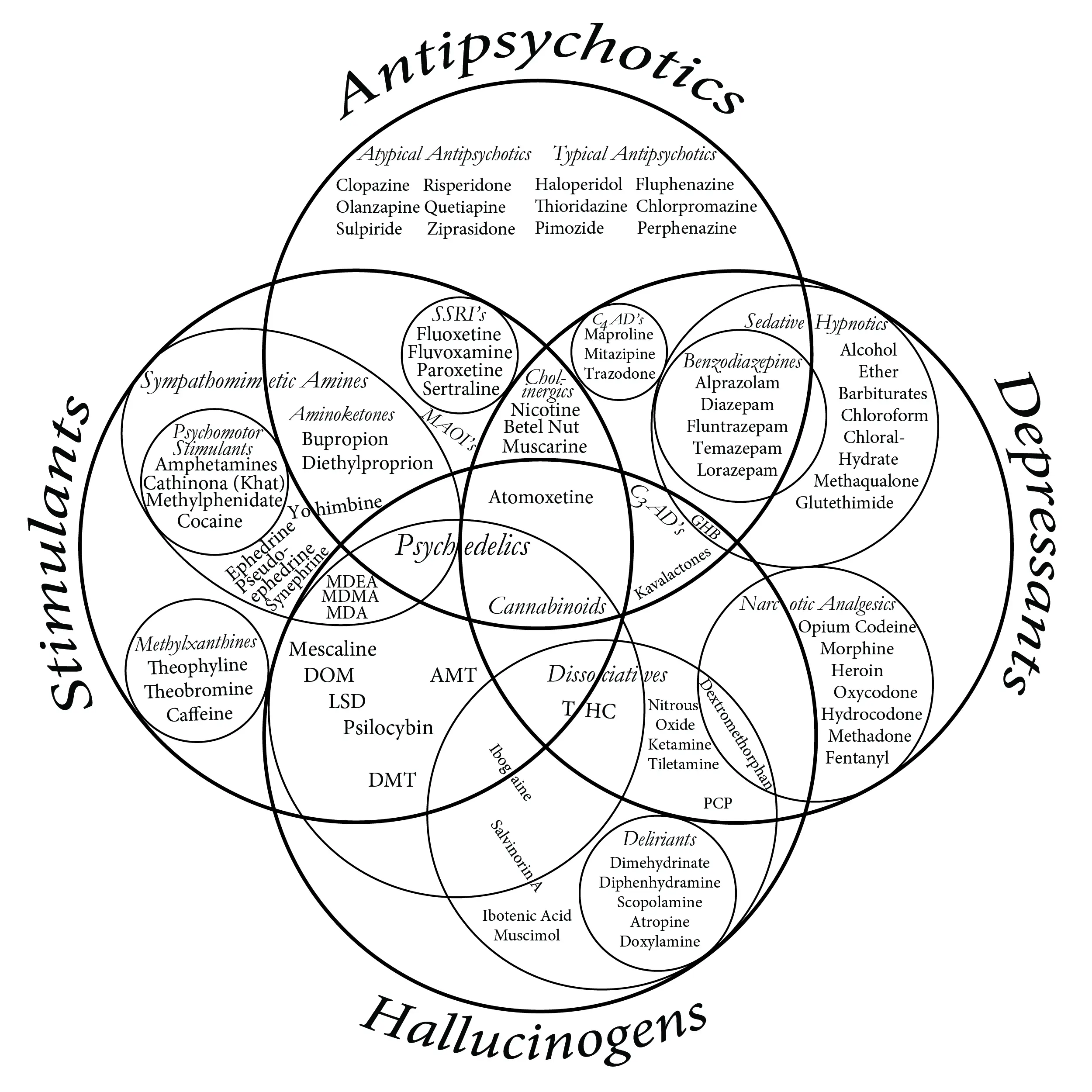
One Representation Of Common Drug Classification (Public Domain Image: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Drug_Venn_Diagram.jpg)